In the world of emails, some land in the main inbox, some end up in spam, and others bounce back. Just like fairytales, our emails face similar journeys when reaching customers. Achieving a 100% inbox placement rate is tough; usually, around 89% of emails make it. Today, we’ll share tips to improve your email delivery and keep them out of spam folders.
Why do my email marketing campaigns keep going to spam?
There could be several reasons, but the most common ones include:
– Spam-like content
– A compromised sender reputation
– Low engagement rates
– Unreliable email infrastructure
– Lack of unsubscribe links
– Non-compliance with email marketing laws like GDPR, CCPA, and CAN-SPAM
– Neglected email lists
– Incorrect or missing email headers
– Failure to meet the latest sender requirements from Google and Yahoo.
Most ISPs have spam filters that determine whether to accept incoming messages. While they might seem like villains, these filters actually safeguard us from phishing attempts, spammers, and harmful emails.
Understanding the mechanics of spam filters
The success of your email campaign greatly depends on filter technology. These filters not only block incoming messages but also categorize them. Nowadays, many email service providers and clients categorize messages into social, commercial, newsletters, and other groups using specific criteria. Similarly, spam filters assess incoming messages and assign them a spam score. If the score surpasses a certain threshold, the email lands in the inbox; otherwise, it’s directed to the spam folder. While the exact criteria are often undisclosed for security reasons, we still have a general idea of what spam filters look for and avoid.
Types of spam filters
Spam filters vary based on the criteria they assess and their implementation methods. Criteria-based filters include:
1. Content filters, which examine incoming messages for spam keywords, harmful attachments, and suspicious HTML code.
2. Header filters, which scrutinize message headers for misleading or infected information.
3. Blacklist filters, which verify if the sender is listed in a blacklist of known spammers.
4. Rule-based or heuristic filters, which evaluate messages based on user-defined criteria like sender-specific triggers or subject line keywords.
5. Permission filters, which confirm if the sender has consent to send marketing emails to the recipient.
6. Challenge-response filters, which send challenges (like entering a password) to verify the legitimacy of the sender.
Implementation-based spam filters include:
1. Gateway filters, which are physical servers detecting phishing, spoofing, malware, viruses, and spam emails at the entry point. Examples include Barracuda, SpamTitan, and Cisco Secure Email Threat Defense.
2. Hosted filters, serving as a secondary security layer. They assess emails after they pass through the gateway filter, assigning a spam score based on content and sender reputation. Examples include Cloudmark, Spambrella, and MailCleaner.
Tips for preventing emails from landing in spam folders across various email providers
Before delving into general recommendations, let’s explore how you can prevent your emails from being flagged as spam across various mailbox providers and email clients.
Gmail:
For senders:
Google offers a set of best practices to enhance inbox delivery for Gmail recipients:
– Configure DKIM and SPF records for your sending domain.
– Set up reverse DNS records (PTR records).
– Ensure your sending domain matches your public website domain.
– Maintain consistent sending from the same IP address.
– Use consistent sender addresses for similar types of emails.
– Avoid combining different email types within a single message.
– Refrain from sending test messages from your primary domain.
– Avoid impersonating others in your emails to prevent them from being marked as spoofed.
For recipients or personal accounts:
If important emails are ending up in your Gmail junk folder, you can whitelist trusted addresses by creating filters or adding them to your contacts:
– To create a filter, go to Settings and then click on “See all settings.”
There, find Filter and Blocked Addresses tab and click Create a new filter.
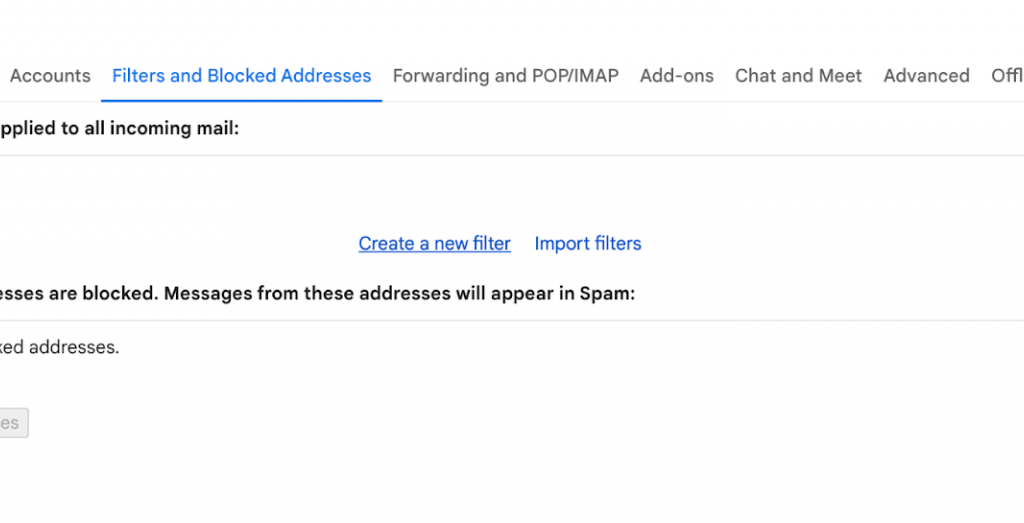
Enter the address you want to be whitelisted in the From field, and type in your own email address in the To field. Press Create filter when you’re done.
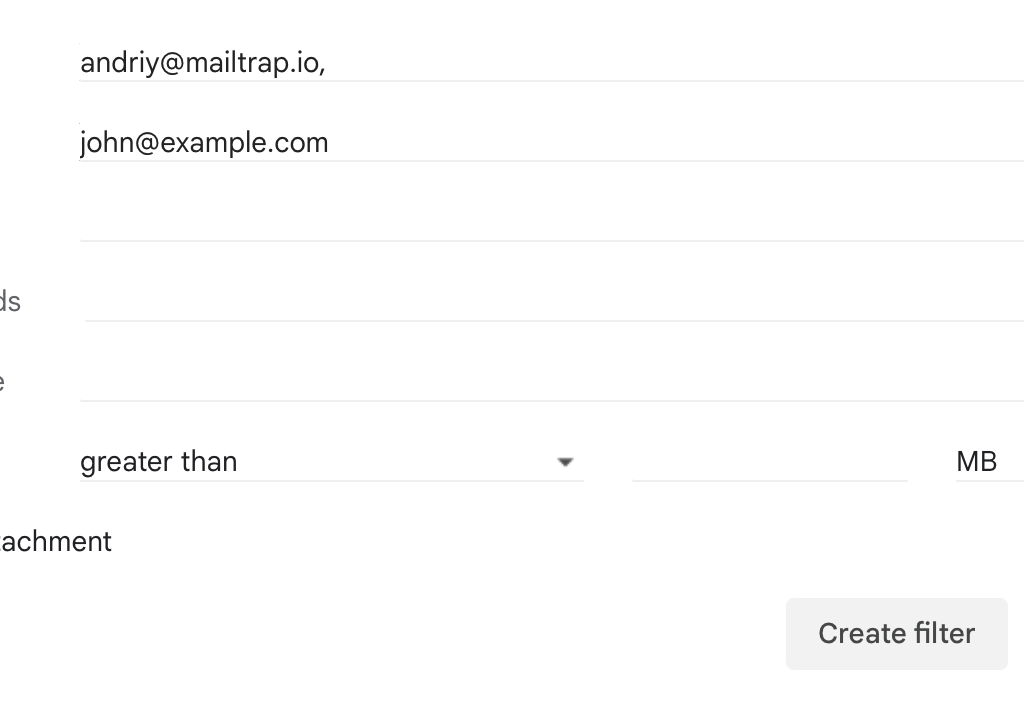
A dialog box will pop up. Mark two checkboxes: Never send it to Spam and Also apply filter to # matching conversations. Then click Create filter.
That’s it. Now the emails from the entered address won’t be marked as spam.
Another option is to add a specific sender to your contacts. For that, find the email from that sender and hover your cursor over the avatar. Press the + sign and the sender will be added to the list of your contacts.
Microsoft Outlook, Hotmail, and Microsoft 365 (former Office 365)
Microsoft doesn’t offer specific instructions on avoiding emails landing in the spam folder like Google does. Here, you can only rely on general recommendations outlined below and encourage recipients to whitelist your sender addresses.
Whitelisting addresses can be done in two primary ways: adding the sender to the safe senders’ list and creating an inbox rule.
To add a sender to the safe senders’ list, you’ll need to access Settings in your Outlook webmail or app. In the web version, click on “View all Outlook settings” (skip this step if you’re using the app).
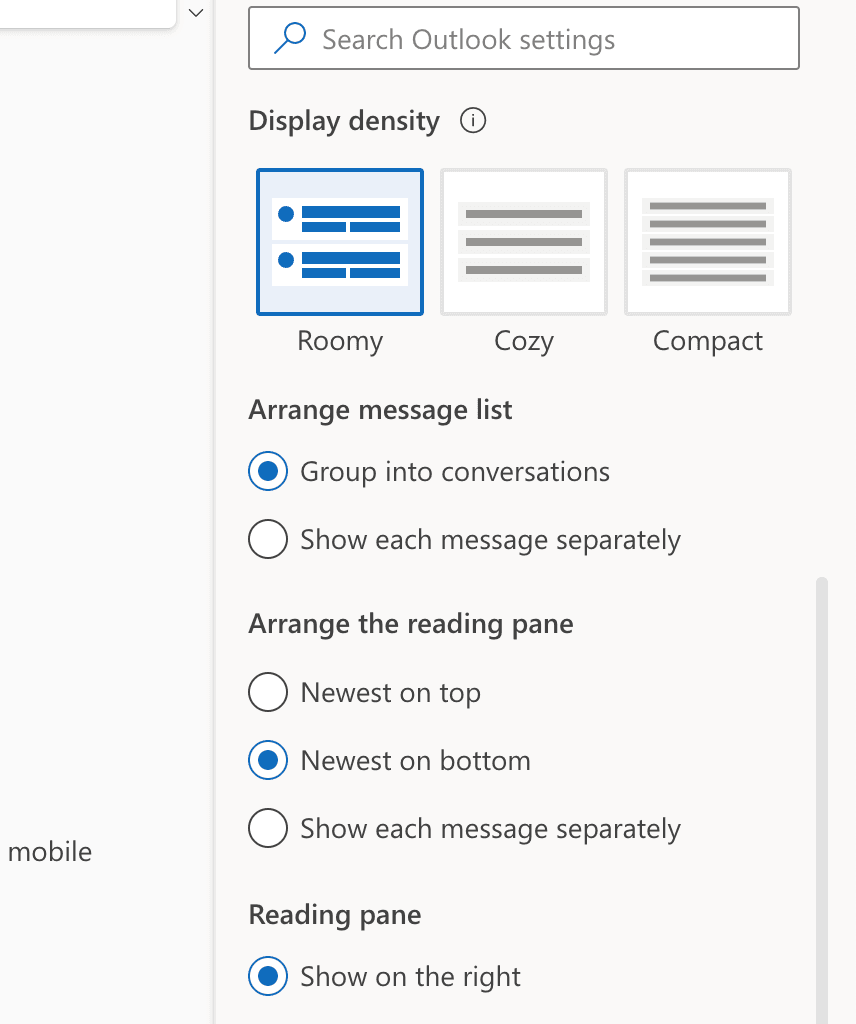
Navigate to Junk email (Junk in the app) and find Safe senders and domains (Safe senders in the app) tab.
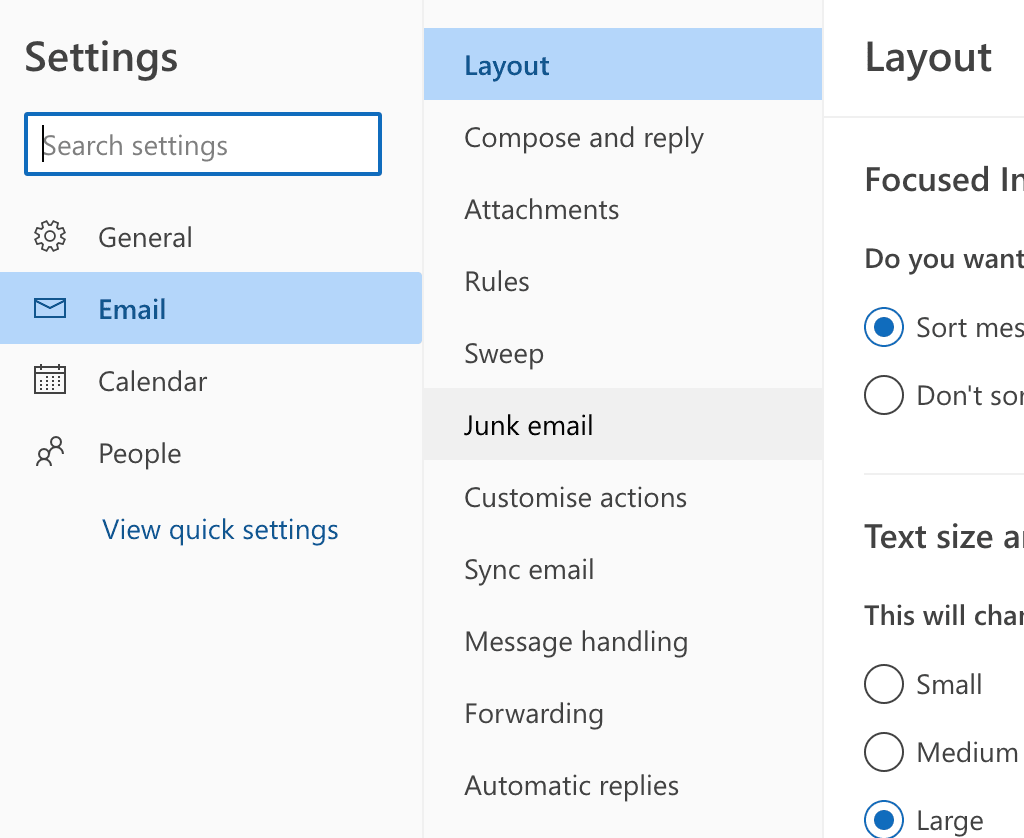
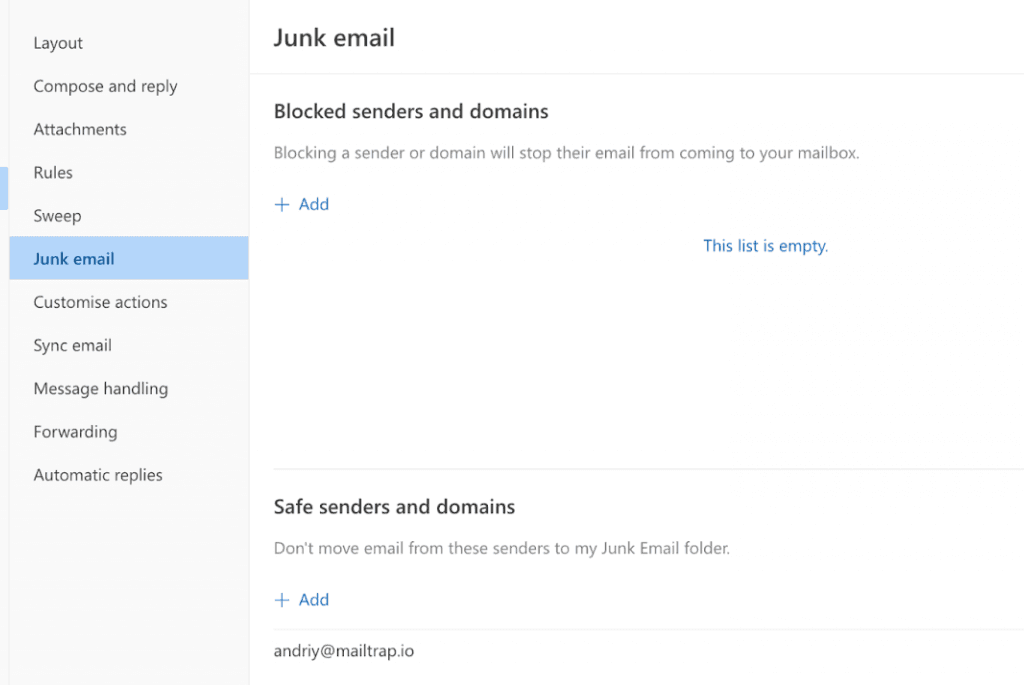
Press +Add (+ icon in the app), type in the sender email address or domain you want to whitelist, and press Enter.
How to avoid emails being marked as spam
As you might expect, there’s no instant fix for dealing with spam filters. It takes deliberate actions to ensure your legitimate emails reach recipients’ inboxes. Below, we’ll guide you on how to lower your email’s spam score and enhance its chances of being delivered to the inbox.
Part 1 - Building a Strong Sender Reputation
Domain Reputation
Email filters evaluate domain reputation based on several metrics:
1. Complaint Rate: This indicates the percentage of emails from your domain reported as spam by recipients. It’s a crucial indicator of your domain’s reputation and email deliverability. A high complaint rate suggests targeting incorrect recipients or delivering poor value. Aim for a complaint rate below 0.1%.
2. Inbox Placement Rate (IPR): This measures the percentage of emails from your domain that land in recipients’ inboxes. It’s a more accurate metric than delivery rate because it focuses solely on inboxed emails. Target an IPR above 80%.
3. Spam Placement Rate: This reflects the percentage of emails from your domain that end up in spam folders. Lower this rate as much as possible, aiming for below 10%.
4. Hard Bounce Rate: This indicates the percentage of emails from your domain that bounce back due to invalid or non-existent recipient addresses. It’s more valuable than the soft bounce rate, which accounts for temporary issues. Aim for a hard bounce rate below 2%.
Email Authentication
Email authentication is crucial for protecting your domain against phishing and spoofing. It relies on four standards:
1. Sender Policy Framework (SPF)
2. DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)
3. Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC)
4. Brand Indicator for Message Identification (BIMI)
Don’t overlook the PTR record, which is a reverse DNS record used by ISPs to verify sender identity.
IP Address Reputation
Similar to domain reputation, factors such as sending volume, engagement rates, spam complaints, and bounce rates influence IP address reputation. Avoid being listed on blocklists, and consider using dedicated IPs for higher sending volumes.
New IP addresses require an “IP warmup” period to establish a reputation gradually and avoid deliverability issues.
Tools to Check Sender Reputation
Several tools help assess sender reputation, including:
1. Sender Score by Return Path
2. Send Forensics
3. Barracuda Reputation Lookup
4. Email Reputation by Cisco’s Talos
Part 2 - Refined Email Content
In the early days of spam filtering, content was the main focus for filters. They scrutinized incoming messages for spam-trigger words, keywords, blacklisted links, and other inappropriate elements. While sender reputation now holds greater importance, content filters remain widely used.
Let’s delve into different aspects of email content and explore how to make them less susceptible to spam by avoiding common mistakes.
Subject Line:
– Steer clear of promotional keywords like “buy,” “sale,” or “discount.”
– Avoid using all capital letters or excessive exclamation points.
– Focus on triggering recipient interest by highlighting product/service features or specifications.
– Personalized subject lines can significantly boost open rates by nearly 50%.
Body Text:
– Ensure readability and minimize grammatical errors to build recipient trust.
– High spelling error rates may trigger content filters, so proofread thoroughly.
– Maintain a balanced text-to-image ratio (60% text to 40% images) to prevent filtering due to large images.
HTML:
– Verify HTML formatting to avoid errors or broken tags, which can trigger spam filters.
– Multi-part messages containing both plain text and HTML can enhance engagement but require careful scrutiny.
Images:
– Limit embedded images to 40% of the total message body to prevent filtering.
– Consider compressing images or linking to them from a web server to reduce message size and processing time.
Attachments:
– Attachments raise red flags for filters due to potential malware or viruses.
– While necessary attachments like invoices are acceptable, avoid unnecessary attachments if possible.
Media Content:
– Overuse of media content can increase spam likelihood and reduce recipient engagement.
– Avoid dynamic scripts, as spam filters typically block them.
Tools for Content Checking:
– Various tools like HTML Email Check or PutsMail by Litmus validate HTML content.
– Email Subject Line Grader or Send Check It test subject lines.
– Tools like Hemingway Editor and Grammarly assist with readability and grammar checks.
– Some email marketing services and ESPs offer built-in content validation tools.
Part 3 – Engaged recipient
Engagement Metrics:
To ensure optimal deliverability, it’s crucial to maintain recipient engagement. Email filters analyze engagement through various metrics:
– Open Rate: The percentage of recipients who open your emails.
– Click-Through Rate: The percentage of recipients who click on at least one link in your email campaign.
– Conversion Rate: The percentage of recipients who complete the desired conversion goal.
– Unsubscribe Rate: The percentage of recipients who unsubscribe from your marketing communications.
Email Formatting:
– Ensure emails open correctly across different clients and devices by previewing them with dedicated tools.
– Optimize loading speed by avoiding large images and dynamic scripts.
– Replace embedded forms with links or CTA buttons to avoid triggering spam filters.
– Check for broken links and refrain from excessive use of colors and fonts, as irregularities may lead to manual spam folder placement.
Email Branding:
– Include the sender’s name in the ‘from’ address and header to reduce spam complaints and increase open rates.
– Consider using a recognizable front person as the email campaign sender, and add “from <your brand>” to the header for credibility.
– Brand other elements such as subject lines, headers, and links for increased recognition and organization.
– Ensure email campaign design and content align with your brand and target buyer personas for consistency and effectiveness.
Follow-ups:
Following up with recipients can enhance your credibility with email filters, showing your commitment to engagement. However, maintaining balance is crucial. Excessive follow-ups in a short period can raise suspicion and lead to emails being flagged as spam. Aim for around once a week or two for follow-ups, maintaining consistency and scheduling campaigns within regular intervals.
Whitelisting:
Emails from contacts’ addresses are less likely to be marked as spam. Encourage recipients to whitelist your main sender addresses if you’re having trouble reaching inboxes. Include instructions in the email for easy whitelisting, as recipients are more likely to comply with minimal effort.
Email Lists:
Building permission-based email lists is essential. Obtain consent from recipients to receive marketing emails, typically through a simple checkbox in sign-up or download forms. Double opt-in, which confirms consent with a confirmation email, is now an industry standard, ensuring a high-quality list of interested contacts.
Unsubscribe Link:
Including an unsubscribe link or button in every commercial email is vital for inbox delivery and legal compliance. The CAN-SPAM Act and similar regulations require senders to disclose the email’s purpose and offer recipients the option to unsubscribe. Ensure unsubscribe links are easily accessible and functional to prevent recipients from marking emails as spam out of frustration.
Quality Over Quantity:
It’s preferable to have a smaller list of engaged recipients than a large list of disinterested contacts. Recipients who can’t easily unsubscribe may resort to marking emails as spam, damaging sender reputation.
Part 4 - Strong Email Infrastructure
Lastly, don’t overlook your email infrastructure. Whether it’s for sending or testing emails, you need a dependable provider. It’s best to choose a platform that offers both solutions in one place, eliminating the need to switch between tools.
One excellent option is Email Jinny. It offers a unified platform for testing emails, sending them to recipients’ inboxes, and monitoring email infrastructure performance. Email Jinny seamlessly integrates two essential solutions: Email Testing and Email Sending.
Email Testing provides a secure space to examine and troubleshoot your emails without inundating users with development clutter. This tool assists you in testing different aspects of your emails to evade spam filters. It accomplishes this through the following features:
Spam Analysis, utilizing SpamAssassin data, enables you to assess the spam score of your emails. If the score exceeds 5, adjustments can be made accordingly. Additionally, detailed descriptions of spam variables are available under the Spam Report chart, with the importance of each highlighted by a score.
In addition, Email Testing provides technical information to view and validate critical email headers. Moreover, it offers the ability to utilize multiple inboxes for various projects, capture all SMTP traffic, automate testing workflows, and preview how your emails will appear on mobile, desktop, and tablet devices.
Once all inspections are completed, you can seamlessly transition to Email Sending. This service offers an Email API and SMTP functionality, ensuring timely delivery to your recipients’ inboxes.
Email Sending provides essential alerts in case of any unforeseen sending issues or unexpected drops in metrics. This ensures you are promptly informed about any issues with your infrastructure, allowing you to take quick and efficient measures.


